Viral gastroenteritis symptoms
Inflammation and irritation of the stomach and intestines are symptoms of viral gastroenteritis. This may result in diarrhea, vomiting, cramps, nausea, and stomach pain. Usually, inflammation brought on by your immune system’s reaction to a bacterial or viral infection is the cause.
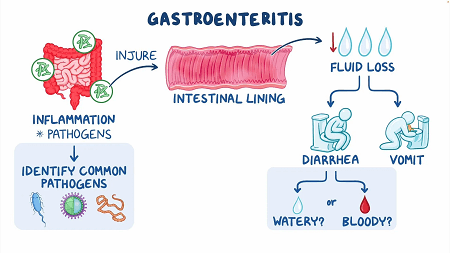
However, gastroenteritis can also result from chemical irritation or infections brought on by fungus or parasites. It’s possible that you’ve heard of “stomach flu.” When people say this, they typically mean viral gastroenteritis. But it has nothing to do with influenza, or the flu, which is a distinct virus that affects the upper respiratory tract (nose, throat, and lungs).
What are the symptoms of viral gastroenteritis?
Gastroenteritis symptoms typically appear soon after infection. For instance, norovirus symptoms usually appear 12 to 48 hours after infection (Trusted Source). Adenovirus symptoms can appear three to ten days following contact.
The duration of symptoms varies from 1 to 14 days, depending on the sort of virus you have received (Trusted Source). Usually, symptoms begin abruptly and last for one or two hours.reliable source.
Symptoms may consist of:
More than three episodes of loose, watery diarrhea per day
chills or a fever
headache, joint aches, muscular aches, or nausea and vomiting
sweaty or clammy skin, pain and cramping in the abdomen, and appetite loss
Viral gastroenteritis typically does not produce bloody diarrhea. A more serious infection may be indicated by blood in your stool.
Symptoms of gastroenteritis usually show up shortly after infection. For example, symptoms of norovirus often manifest 12 to 48 hours following infection (Reliable Source). Three to ten days after contact, adenovirus symptoms may manifest.
Depending on the type of virus you have, symptoms might last anywhere from one to fourteen days (Reliable Source). Symptoms typically start suddenly and go away in an hour or two.trustworthy source.
Symptoms could include:
More than three bouts of loose, watery diarrhea per day, fever, chills, headache, joint, or muscle aches, nausea, vomiting, hot or clammy skin, abdominal pain and cramping, and loss of appetite
In most cases, bloody diarrhea is not a symptom of viral gastroenteritis. Blood in your stool could be a sign of a more serious ailment.
What causes viral gastroenteritis?
Gastroenteritis can be caused by several viruses. People who are afflicted can have viruses in their feces and vomit. It has a long lifespan outside of the body. Infected individuals can transfer the virus to anything they come into contact with, particularly if they don’t wash their hands after using the restroom. Infected food workers can infect others by contaminating food and beverages. The disease can also be spread by sewage that enters the water supply. The stomach flu is another name for viral gastroenteritis. However, it is not brought on by the influenza virus, which causes seasonal flu.

Viruses that frequently cause gastroenteritis include:
- Rotavirus. Infants aged 3 to 15 months are most frequently infected by this virus. The disease is more prevalent in the fall and winter and lasts for three to seven days.
- Norovirus. The most frequent cause of illnesses in adults is this virus. On cruise ships, it frequently causes breakouts. The symptoms can appear at any time of year and continue for one to three days.
- Adenovirus. Children ages 2 and under are susceptible to this virus, which is present all year round. The duration of symptoms is 5–12 days.
Viral gastroenteritis can also be caused by a variety of different viruses.
Self care
Try the following to stay more comfortable and avoid dehydration during your recuperation:
- Give your stomach time to settle. Take a few hours off from eating solid foods.
- Try frequently drinking little sips of water or sucking on ice chips. Additionally, you may try clear broths, clear soda, or non-caffeinated sports drinks. Oral rehydration solutions may be an option in some situations. Consume a lot of liquids each day by taking tiny, regular sips.
- Return to eating gradually. You can resume your regular diet as soon as you are able. At first, you may be able to consume bland, easily digested items like rice, soda crackers, soup, oats, noodles, and bananas. If you feel queasy again, stop eating.
- Until you feel better, stay away from specific foods and drugs. These include foods that are fatty or heavily seasoned, alcohol, nicotine, and caffeine.
- Make sure you get enough sleep. You may have been weak and exhausted from the illness and dehydration.
- Try using anti-diarrhea drugs. To control their symptoms, some people may find that using bismuth subsalicylate (Pepto-Bismol, for example) or loperamide (Imodium A-D) is beneficial. Avoid these, though, if you have fever or bloody diarrhea, as these could indicate another illness.
Treatment for gastroenteritis
Depending on the cause, treatment options could include:
- Drink lots of water.
- You can get oral rehydration liquids from your pharmacist.
- In extreme situations, hospitalization and intravenous fluid replacement may be necessary.
- If the cause is bacteria, antibiotics.
- medications to eradicate the parasites, if they are the cause.
- Unless your doctor prescribes or recommends it, stay away from anti-vomiting or anti-diarrhea
- treatments as they will maintain the infection inside your body.
Where to get help
- Your general practitioner
- For professional health information and guidance, call Nurse-on-Call at 1300 606 024 (24 hours, 7 days a week).
- The communicable disease epidemiology and surveillance unit of the Department of Health, Victorian Government, can be reached at 1300 651 160 through your local council’s health department.