Vaginal thrush
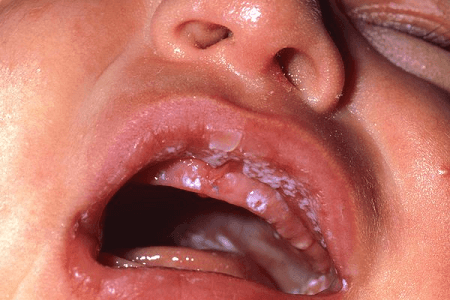
A fungal (yeast) infection called Thursh can develop in your throat, mouth, and other areas of your body. Oral thrush, also known as oral candidiasis, can cause white, elevated lesions (spots) on your tongue and cheeks that resemble cottage cheese. Thrush can quickly aggravate, resulting in redness and soreness in the mouth.
Thrush caused an overabundance of the fungus Candida. Oropharyngeal candidiasis is another term for thrush in the throat or mouth.
Medical professionals use antifungal drugs to treat thrush. Thrush is a mild issue that disappears a few weeks after you begin treatment if your immune system is functioning normally.
Symptoms of Thursh
Adults and children
At first, you might not even be aware that you have oral thrush. Symptoms and indicators could include:
- Creamy white spots on your tongue, inner cheeks, and occasionally the tonsils, gums, and roof of your mouth
- Lesions that resemble cottage cheese and are somewhat elevated
- Redness, burning, or discomfort that could be so bad that it makes it hard to swallow or eat
little bleeding in the event that the lesions are scraped or scratched - Redness and cracking at your mouth’s corners
- A sense of cottoniness in your mouth
- Taste loss
- Redness, burning or soreness that may be severe enough to cause difficulty eating or swallowing
- Slight bleeding if the lesions are rubbed or scraped
- Cracking and redness at the corners of your mouth
- A cottony feeling in your mouth
- Loss of taste
- Redness, irritation and pain under dentures (denture stomatitis)
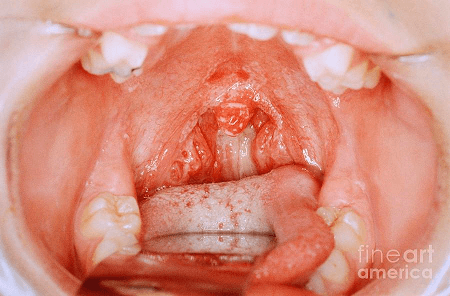
In severe cases, usually related to cancer or a weakened immune system from HIV/AIDS, the lesions may spread downward into your esophagus — the long, muscular tube stretching from the back of your mouth to your stomach (Candida esophagitis). If this occurs, you may experience difficulty swallowing and pain or feel as if food is getting stuck in your throat.
What causes thrush?
You are more likely to have thrush if:
Your skin is injured or irritated.
You’re on antibiotics.
You have poorly managed diabetes; you have a compromised immune system, such as while undergoing hormone replacement therapy (HRT) or chemotherapy; or you are living with HIV.
During pregnancy, you utilize skin-irritating goods including vaginal wash products, bubble baths, and perfumed products.

How is thrush treat?
Your symptoms, age, and overall health will all affect how you are treat. The severity of the ailment will also determine this.
Early treatment of thrush is crucial to reducing discomfort and difficulty swallowing as well as halting the development of infection.
Brushing the affected areas daily to remove the coating may be sufficient to treat and manage a very mild case of Thursh.
The most common treatment for thrush is an antifungal medication. These medications may taken as pills. Alternatively, they could be applied topically to your throat and mouth. They could consist of an antifungal lozenge or a swirl and swallow medication. They go after the overgrowth of Candida.
If the thrush doesn’t respond to topical treatment, your healthcare provider will likely switch treatment to an antifungal pill. This medicine is often stronger against Candida. It will also treat it in multiple locations in the body if necessary. The length and type of your therapy will depend on several factors. These include the severity of your infection and any other health problems. In rare cases, you may need to take medicine through an IV.
Some people may also need ongoing preventive treatment with oral antifungal medicines. You might need them if you are at continued high risk for thrush.
Your healthcare provider will also be trying to find out if the thrush developed because of an underlying reason. They may suggest changes that will help cure the thrush faster and help prevent it from happening again.
Prevention about Thursh
Oral thrush can avoided in the following ways:
Maintain proper dental hygiene: Use fluoride toothpaste to brush your teeth at least twice a day, floss every day, and rinse your mouth after eating.
If you use dentures, make sure they fit correctly, clean them every day, and take them out at night.
Manage the underlying circumstances: Make sure your blood sugar is under control if you have diabetes.
Steer clear of specific mouthwashes: Thrush may result from antiseptic mouthwashes altering the delicate balance of oral flora.
Cut back on sugar: Limit your intake of foods that include sugar and yeast.
Give up smoking: The symptoms of thrush can worsen if you smoke.
Use a soft toothbrush: To prevent damaging your mouth’s mucous membranes, use a soft toothbrush.
Consume probiotics to assist your mouth’s bacterial balance return to a healthy level.
Treating a vaginal yeast infection as soon as feasible is important. Fluconazole can taken in a single dose of 150 mg, which works similarly to creams or suppositories. However, if you are pregnant or using other medications, you should see your doctor or pharmacist before taking oral medication.